Mansha Clinic
Home > Paediatric Facilities
Mansha Clinic, New Delhi delivers up-to-the-minute care to children with challenging clinical conditions. These facilities are provided by a knowledgeable and trained expert who is skilled in several fields of Paediatrics.

Consultation Available at Mansha Clinic for Children are:
- New Born & Child Illness
- Asthma & Allergic Conditions
- Adolescence related issues
- Nutrition & Feeding Issues
- Emergency Medicine
- Neonatal care
- Chronic Childhood Diseases and Disorders
- Growth and Developmental Delay
- Obesity in Children and more

Facilities we offer
1. Nebulization

Nebulization is a process of respiratory care. It is the medical procedure of conducting medication directly by inhalation, with the help of a nebulizer device that transforms liquid medicine into mist, which is then given to the child with the help of a breathing mask. Nebulization is typically administered children with Asthma, COPD and children needing respiratory care for other breathing problems and is incompetent to use inhalers. Nebulization is occasionally also advised for severe cases of nasal and chest congestion.

The advantages of nebulization are as follows:
- Nebulization therapy comes in handy for little kids who are not able to use any other inhalation device.
- Nebulization is extremely helpful in a severe asthma attack situation.
- Comparatively easy to use, and much easy to coordinate (just breathe normal).
- Simple to inhale the medicine, despite of airflow limitation caused by flare-ups and end stages of COPD.
2. Immunization & Vaccination
Immunization, being one of the highly valuable inventions in human life till date, is an important feature of Paediatrics, for elimination of diseases in children. Highlighting importance of prevention of communicable diseases in your kids, Immunization (vaccination) is a process to create immunity to (protection from) some diseases. This is performed by using small quantity of a killed or weakened germ that causes the disease. Germs can be viruses or bacteria (such as measles virus and pneumococcus bacteria). Vaccines encourage the immune system to react as if there were a real infection. It blocks the “infection” and remembers the germ. Then, it would fight the germ if it enters the body again.
Vaccines Available for children are:

BCG (TB)
The BCG (Bacillus Calmette–Guérin) vaccine helps your child's immune system confront the germs that produce TB and helps stop them from getting serious Tuberculosis disease.

Polio (Oral & Injectable)
Polio vaccines are vaccines helps to prevent poliomyelitis. Two types of vaccines are used: an inactivated poliovirus (IPV) given by injection and a weakened poliovirus (OPV) given by mouth.

DPT (Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus)
It is a vaccine that guard children younger than age 7 originate immunity to three lethal diseases caused by bacteria: diphtheria, tetanus, and whooping cough (pertussis).

HIB (Influenza)
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) disease is a serious disease originated by bacteria. Hib vaccination is recommended for all children younger than 5 years of age as the germs spread from person to person

Hepatitis A & B
Hepatitis A and hepatitis B are viruses that attack the liver. The combination hepatitis A and B vaccine produce immunity for a minimum of 10 years and possibly for a lifetime when completing the full series

Typhoid
Typhoid vaccine protects from bacterial infection caused by contaminated food and water. Symptoms of infection include constipation, high fever, headache, tiredness, loss of appetite, dizziness, cough

Pneumococcal
The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine protects against the most common kinds of pneumococci bacteria. It is recommended for all newborn and children starting at 2 months of age. It contains 13 types of pneumcoccus.

Meningococcal
The meningococcal conjugate vaccine protects against four types of meningococcal bacteria (called types A, C, W, and Y). A full course of the meningococcal conjugate vaccines should be provided to kids and teens.

MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella)
The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine is advised for all children. It shields against three serious illnesses. In most states, you must prove your children have received it before they can enter school.

Rota Virus
Rotavirus disease is highly contagious, this virus causes severe acute gastroenteritis with diarrhoea and vomiting, primarily in infants and young children. The virus is present in the stool of an infected person and can remain effective for a long time.

Chicken Pox
Chickenpox is a very contagious infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus. You can protect your child from chickenpox with a vaccine, children should get 2 shots for chickenpox: the first when they are 12 to 15 months old followed by a “booster” shot once they are 4 to 6 years of age.
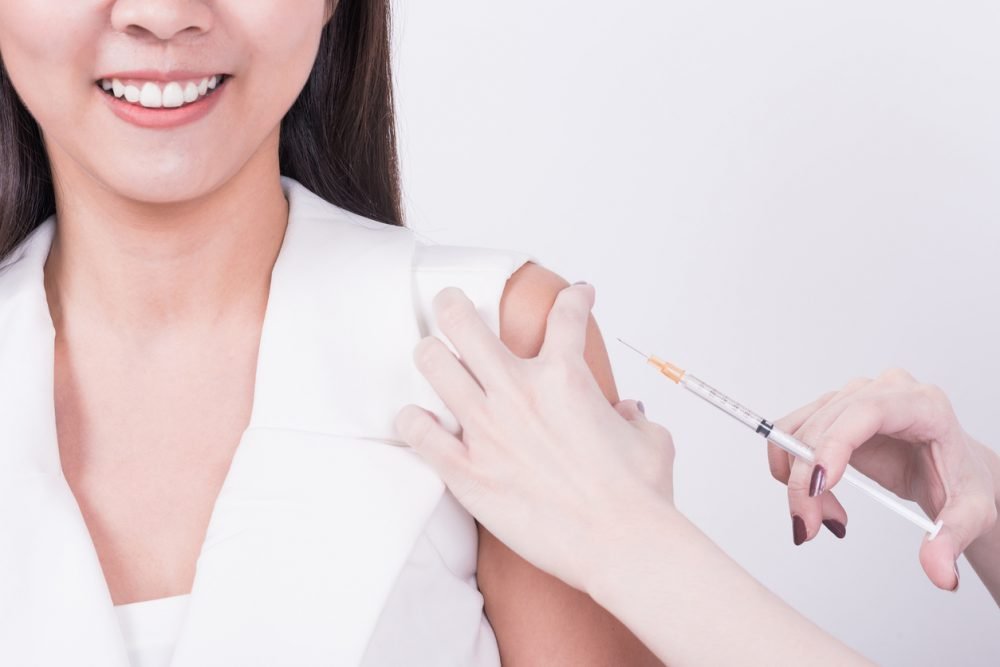
HPV (Cervical Cancer Vaccine)
Cervical cancer is the fifth most common cancer in humans. Girls and boys should get two shots of HPV vaccine at the minimum of 6 months apart at ages 11 or 12, finishing the two-shot series before their 13th birthday.

Swine Flu
There are different types of swine flu vaccine for babies available. However, the flu vaccine cannot be provided to babies younger than six months. It is recommended to have a discussion with doctor on getting vaccinated for swine flu even for the entire family.

Dog Bite
Rabies is a viral infection that attacks the nervous system. A child may get rabies if he or she is bitten or scratched by an animal with rabies. The virus can also be developed if a child has scratches or sores that are licked by an infected animal.

